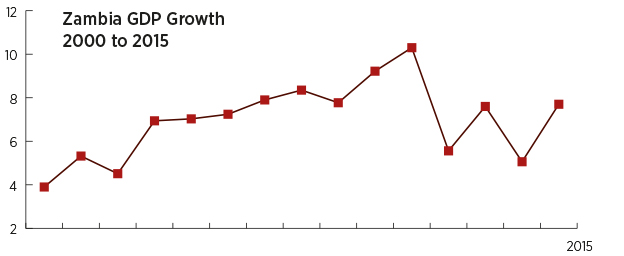
Considered one of the world’s fastest growing economies for ten years until 2014, Zambia had a GDP growth rate averaging 6.7% per year thanks to its copper production and political stability. Zambia is the world’s eighth largest producer of copper, second only to the Democratic Republic of Congo.

The economy of the country heavily relies on the mining industry as the sector accounts for over 70% of export earnings. Home to the Victoria Falls, one of the world’s Seven Wonders, the country has a thriving tourism economy. Agriculture employs 61% of the labour force, while it represents 7% of GDP. Falling copper prices, reduced power generation and depreciation of the kwacha slowed the economy’s growth between 2015 and 2017.
Landlocked but well connected, Zambia has managed to avoid wars and conflicts after its independence. Its population of 16 million is set to triple by 2050, as projected by the UN. It offers access to several key markets such as the COMESA, representing a market of 580 million people. As a member of the Southern African Development Community, Zambia is part of a free trade area.
MINING
Zambia has a century-long history in mining and quarrying. The industry accounts for about 12.9% of the country’s GDP. As the world’s eighth largest copper producer, Zambia holds 6 percent of the world’s known copper reserves. Its main activities are established in the Copperbelt and the North-Western Province, home to the biggest mines. Copper and cobalt, the country’s traditional exports, account for well over 70 percent of export earnings. Other minerals include gold and gemstones (e.g. emeralds, aquamarine, topaz, opal, agate and amethysts). Zambia produces over 20% of the world’s emeralds. This extensive range of mineral resources, including a variety of industrial minerals, and energy resources including uranium, coal and hydrocarbons, presents excellent investment opportunities in the extraction and processing of these minerals in the country.
AGRICULTURE
Second to mining, agriculture constitutes an important part of Zambia’s GDP at 9.5%. Zambia is endowed with a large arable land resource base of 42 million hectares, of which only 1.5 million hectares are cultivated every year. It has abundant water resources for irrigation, and the country accounts for 40 percent of the water resource in the Southern Africa Development Community (SADC). Given the vast resource endowment in terms of land, labour and water, Zambia has huge potential to expand its agricultural production.
The country has a total land area of 75 million hectares (752,000 square Km), which is divided into three major agro-ecological regions, namely Regions I, II and III – each suitable for investment opportunities in the production of various crops.
Zambia’s climate follows a pattern similar to that of most southern Africa countries, with rainfall when the sun is near its zenith from November to April.
Despite the vast arable land, plenty of water and the fact that the agricultural sector employs more than half of the total labour force, only 10 percent of the arable land is under cultivation. It is due to this potential that the government encourages investment in commercial farming and has established farm blocks to facilitate investments in agriculture. With vast stretches of land suitable for agriculture, the government has embarked on improving access to inputs and finance for small scale farmers as a way of diversifying the economy from a heavy reliance on copper production and exports.
A number of initiatives have been taken to get farmers to diversify, moving away from cultivating traditional maize, encouraging the cultivation of soya beans, cow peas, groundnuts, mixed beans and cassava. These crops offer a huge potential source of revenue as they are of high value and are currently produced in small quantities.
Manufacturing
 The manufacturing sector accounts for nearly 11% of the country’s GDP and has been growing at a steady pace. However, the sector needs to produce a wide range of high-quality value-added intermediate and final products for the export markets. Engineering, textiles, wood & wood products, building materials, processed foods, chemicals, leather and leather products and handicrafts offer potential opportunities for investments. Currently, the main manufacturing activities in Zambia are the food, beverages and tobacco sub-sector. Support measures designed to aid manufacturing enterprises in non-traditional sectors are being implemented.
The manufacturing sector accounts for nearly 11% of the country’s GDP and has been growing at a steady pace. However, the sector needs to produce a wide range of high-quality value-added intermediate and final products for the export markets. Engineering, textiles, wood & wood products, building materials, processed foods, chemicals, leather and leather products and handicrafts offer potential opportunities for investments. Currently, the main manufacturing activities in Zambia are the food, beverages and tobacco sub-sector. Support measures designed to aid manufacturing enterprises in non-traditional sectors are being implemented.
Tourism
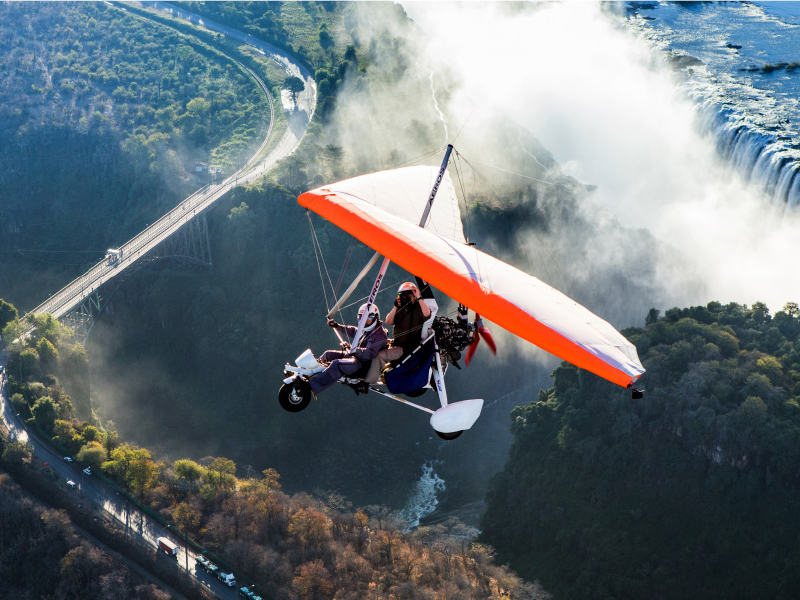 The tourism industry has grown in recent years, with the establishment of hotels in the major tourist town of Livingstone and the city of Lusaka. The vast potential in the tourism sector in Zambia, with its natural beauty (including the Victoria Falls, which is one of the most renowned beautiful transcendental Seven Natural Wonders of the World) and the wealth of wildlife have yet to be fully exploited. Zambia has 20 national parks and 34 game management areas with a total of 65,000 km2 set aside for wildlife conservation. Zambia also boasts of various traditional ceremonies that take place at different times of the year where the rich cultural heritage is displayed.
The tourism industry has grown in recent years, with the establishment of hotels in the major tourist town of Livingstone and the city of Lusaka. The vast potential in the tourism sector in Zambia, with its natural beauty (including the Victoria Falls, which is one of the most renowned beautiful transcendental Seven Natural Wonders of the World) and the wealth of wildlife have yet to be fully exploited. Zambia has 20 national parks and 34 game management areas with a total of 65,000 km2 set aside for wildlife conservation. Zambia also boasts of various traditional ceremonies that take place at different times of the year where the rich cultural heritage is displayed.
Railway, Roads and Aviation Infrastructure
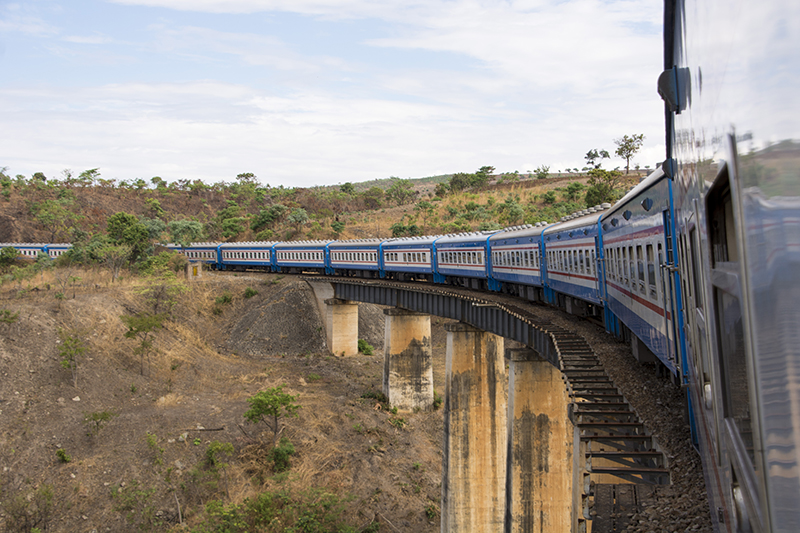 Zambia is dominated by rail network transport and major infrastructure works are underway, including the Chipata-Mchinji Railway, linking Zambia with Malawi and Mozambique. Major road constructions lie ahead with the Accelerated National Roads Construction Programme, accounting for 8,000 km of construction by the private sector.
Zambia is dominated by rail network transport and major infrastructure works are underway, including the Chipata-Mchinji Railway, linking Zambia with Malawi and Mozambique. Major road constructions lie ahead with the Accelerated National Roads Construction Programme, accounting for 8,000 km of construction by the private sector.
Energy
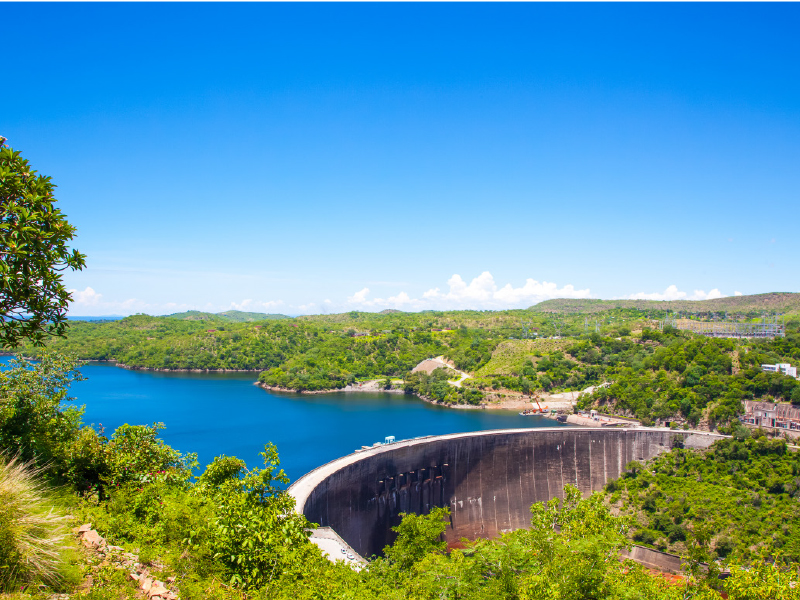 With its vast water resources and coal reserves, Zambia offers abundant investment opportunities for hydro and thermal electricity power generation, supply and distribution. The country has well over 1,890 MW of hydroelectric generating capacity. Proven coal reserves exceed 30 million tonnes and satisfy 9% of energy demand. Hydro-electricity is mainly supplied and distributed by the state-owned Zambia Electricity Supply Corporation (ZESCO). There is massive potential for private sector investment in hydroelectricity power generation, transmission and distribution, and supply of petroleum products, including bio-fuels.
With its vast water resources and coal reserves, Zambia offers abundant investment opportunities for hydro and thermal electricity power generation, supply and distribution. The country has well over 1,890 MW of hydroelectric generating capacity. Proven coal reserves exceed 30 million tonnes and satisfy 9% of energy demand. Hydro-electricity is mainly supplied and distributed by the state-owned Zambia Electricity Supply Corporation (ZESCO). There is massive potential for private sector investment in hydroelectricity power generation, transmission and distribution, and supply of petroleum products, including bio-fuels.
Telecommunications
 Zambia has access to the West Coast Sat-3 cable to Europe via a fibre link with Namibia, which in turn links with the South African fibre network, reaching Cape Town. Currently three companies, the Zambia Electricity Supply Corporation (ZESCO), the Copper belt Energy Corporation (CEC) and the Zambia Telecommunications Company (ZAMTEL) are licensed to operate optic fibre networks, and there are three (3) mobile telephone services, namely Airtel Zambia, MTN and Zamtel.
Zambia has access to the West Coast Sat-3 cable to Europe via a fibre link with Namibia, which in turn links with the South African fibre network, reaching Cape Town. Currently three companies, the Zambia Electricity Supply Corporation (ZESCO), the Copper belt Energy Corporation (CEC) and the Zambia Telecommunications Company (ZAMTEL) are licensed to operate optic fibre networks, and there are three (3) mobile telephone services, namely Airtel Zambia, MTN and Zamtel.
Health
 Government and private hospitals and clinics provide health care. The private hospitals have earned a reputation as providers of good quality healthcare. Major surgery cases are usually referred to the Republic of South Africa. Investment opportunities for establishing specialised hospitals to treat such referral cases are, therefore, unexploited. Flying doctor services cover remote areas and provide immediate care and transport for urgent cases.
Government and private hospitals and clinics provide health care. The private hospitals have earned a reputation as providers of good quality healthcare. Major surgery cases are usually referred to the Republic of South Africa. Investment opportunities for establishing specialised hospitals to treat such referral cases are, therefore, unexploited. Flying doctor services cover remote areas and provide immediate care and transport for urgent cases.
Education
 There are currently only 3 public universities, namely the University of Zambia, the Copperbelt University and the Mulungushi University, and numerous private universities which include, but are not limited to, Cavendish University, the Zambia Open University, the University of Lusaka, Catholic University and many more. There are also over 40 technical colleges. In short, there are tonnes of investment opportunities for the provision of university-level and other tertiary education.
There are currently only 3 public universities, namely the University of Zambia, the Copperbelt University and the Mulungushi University, and numerous private universities which include, but are not limited to, Cavendish University, the Zambia Open University, the University of Lusaka, Catholic University and many more. There are also over 40 technical colleges. In short, there are tonnes of investment opportunities for the provision of university-level and other tertiary education.
![[:en]MANUFACTURING[:]](https://perspectives-cblacp.eu/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/MANUFACTURING-696x522.jpg)


