WHY EIP – RATIONALE AND BACKGROUND
EIP – WHY
The Sustainable Development Goals
On September 25th 2015, countries adopted a set of goals to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure prosperity for all as part of new sustainable development agenda. Each goal has specific targets to achieve over the next 15 years.
The Investment gap
The estimated global investment gap in key SDG sectors, 2015 –> 2030 are trillions of USD, annual average. The Official Development Aid (ODA) alone cannot cover this gap. Consequently, the European Union Institutions need to partner with the private sector in order to cover it.
- Total Annual investment needs = 3.9 trillions of USD
- Current Annual Investment = 1.4 trillions of USD (2020 figures)
- Total Investment Gap = 2.5 trillions of USD/year (2014 UNCTAD)
EIP – GOALS
- Contribute to Sustainable Development
- Improve Investment climate
- Encourage investment (especially private)
- Tackle root causes of irregular migration
- Focus on jobs and growth
EIP – HOW
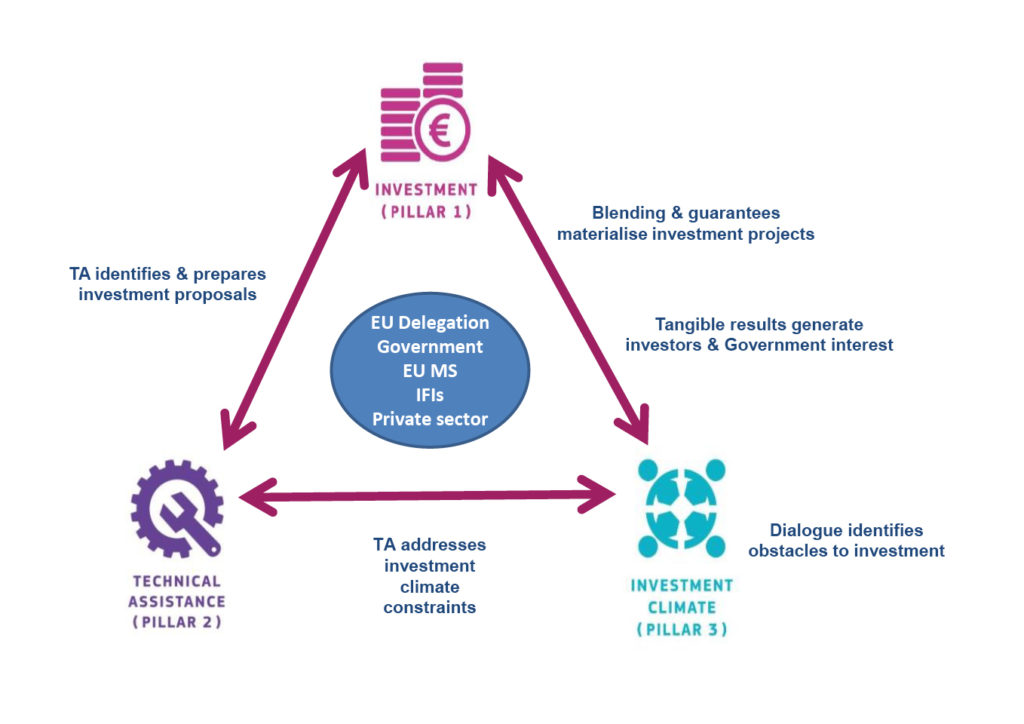
EIP’s Integrated Approach: the 3-Pillar Structure. It is a one-stop-shop for public and private investors.
Pillar I – European Fund for Sustainable Development (EFSD)
- New guarantee to reduce risk
- Blending loans and grants (Africa Investment Platform, EU Neighbourhood Investment Platform)
EFSD guarantee
- A risk mitigation mechanism to stimulate investments in Africa and in the Neighbourhood
- Will leverage additional financing, in
particular from the private sector (crowding in), by reducing the risk - A guarantee capacity for credit enhancement will ultimately benefit the final investments
- Will provide liquidity from its guarantee fund (liquidity cushion)
What is Blending?
It is a strategic use of a limited amount of EU financial support in order to mobilise financing from partner International Financial Institutions (IFIs) and other sources (including private sector) and enhance the development impact of investment projects as long as this EU support is “additional”. This means otherwise the project would not materialise or would materialise in a sub-optimal way.

*EU contribution vs funding by IFIs, private and public sector
Pillar II – Technical Assistance (TA)
- Support local authorities and companies preparing bankable projects
- Improving the investment climate in close engagement with the Private Sector
What is Technical Assistance?
- Provision of know-how: training, short and long-term personnel, research, policy and advisory services, studies, communication or knowledge sharing
- Typically a TA project could also include other support activities: supplies and equipment, visibility, works…
- Ownership by partner government, through Steering Committees
- Supported by specialised consulting firms and agencies
Pillar III – Investment climate
- Structured dialogue with business
- Market Intelligence & Analytics
- Policy and political dialogue
- EU Cooperation
EIP INTEGRATED APPROACH – This is how the dots connect
NDICI – GLOBAL EUROPE
EIP has ambitious plans for the future.The European Commission is aiming to achieve a more efficient financial architecture for investment outside the European Union. The new investment architecture is the Neighbourhood, Development and International Cooperation Instrument (NDICI) also known as Global Europe.
The NDICI combines all EU external action programmes into one broad financing tool. This new instrument is made of three main components (geographical, thematic and rapid response) and a more flexible element to counter emerging crises. Funds can easily be shifted from one issue to another within the broader scope of the instrument. It also provides a more policy-driven and inclusive approach, with potentially more direct input from local and national stakeholders. The new instrument can help closing gaps and avoiding overlaps in the multitude of EU external programmes. This means that EU policies focusing on poverty reduction, protection of human rights and crisis response would now all be financed via this single instrument.
In a nutshell, the NDICI Global Europe’ objective is to uphold and promote the Union’s values and interest worldwide via
- Simplification
- Consistent and flexible approach
- Rapid response and programmed cooperation
It is the main instrument for EU cooperation and development with partner countries.
NDICI – GLOBAL EUROPE – STRUCTURE
NDICI – GLOBAL EUROPE – Features

Source:
EIP website: https://ec.europa.eu/eu-external-investment-plan/home_en
NDICI related: EU – Private sectors consultations slides (May 2021)
![[:en]shutterstock_378626257[:]](https://perspectives-cblacp.eu/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/shutterstock_378626257-696x464.jpg)